You can create a Frontend component that takes up the full viewport of a browser (also known as full-bleed). Let's look at an example of how to do this.
Below is an example of a hero Frontend component. The image can either be the full width of the grid or the full width of the viewport.
| Full width of grid (12-column layout element) | Full width of viewport (full-bleed) |
|---|---|
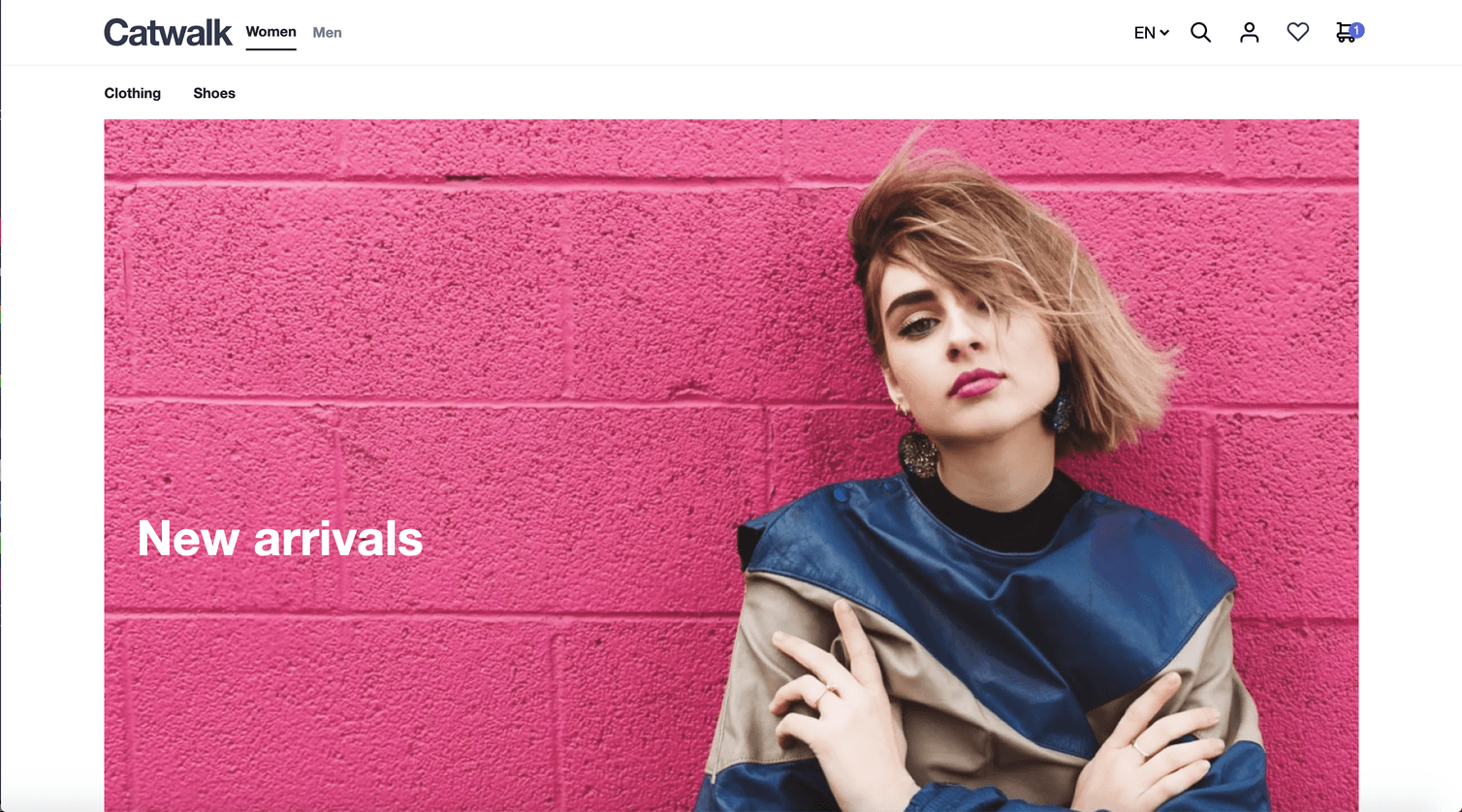 |  |
Build a full-width component
As always, we start with the schema. We will create a text field and a toggle so that Studio users can turn our full-bleed image feature on and off. We have also configured a maximum use per page; as a result, you can add the image only once to a page.
{
"tasticType": "frontastic/examples/hero",
"name": "Hero",
"icon": "image",
"category": "content",
"maxUsePerPage": 1,
"schema": [
{
"name": "Content",
"fields": [
{
"label": "Image",
"field": "image",
"type": "media"
},
{
"label": "Full-bleed?",
"field": "isFullBleed",
"type": "boolean",
"required": true,
"default": true
},
{
"label": "Aspect ratio",
"field": "aspect",
"type": "enum",
"default": "16/9",
"values": [
{
"value": "original",
"name": "Original"
},
{
"value": "16/9",
"name": "16:9"
},
{
"value": "4/3",
"name": "4:3"
},
{
"value": "21/9",
"name": "21:9"
}
]
}
]
}
]
}
Upload this schema to the Studio.
index.tsx file to receive the information from the schema.import React from 'react';
import Hero from 'components/Hero';
const HeroTastic = ({ data }) => {
return <Hero {...data} />;
};
export default HeroTastic;
frontend/components/HOC/. This simple React Component makes sure its contents (the children) fill up the whole horizontal viewport space. To accomplish this, we use a little CSS trick.import React from 'react';
export default function FullPageWidthWrapper({ children, className = '' }) {
return (
<div
className={className}
style={{
width: '100vw',
position: 'relative',
left: '50%',
right: '50%',
marginLeft: '-50vw',
marginRight: '-50vw',
}}
>
{children}
</div>
);
}
index.tsx of the component.import React from 'react'
import Image from 'frontastic/lib/image';
import FullPageWidthWrapper from '../Layout/FullPageWidthWrapper'
const Hero = ({ image, aspect, isFullBleed }) => {
const aspectClass = {
'original': '',
'16/9': 'pb-16/9',
'4/3': 'pb-4/3',
'21/9': 'pb-21/9',
}
const calculateAspectStyle = (aspect, img) => {
if (aspect === 'original' && img) {
return { paddingBottom: '${(img.media.height / img.media.width) * 100}%'}
}
return {}
}
const content = (
<div className={'relative ${aspectClass[aspect]}'} style={{...calculateAspectStyle(aspect, image)}}>
<Image media={image} className={'w-${isFullBleed ? 'full' : 'auto'} absolute'} alt="Logo" />
</div>
)
if (isFullBleed) {
return <FullPageWidthWrapper>{content}</FullPageWidthWrapper>
}
return content
}
export default Hero
And that's it. When you add this component to a page version in the Studio, you can select the image and if it is full-bleed:

If you add another Frontend component to the same layout element, it could cause your layout to break. Either keep it in a separate layout element or update your CSS to stop this from happening.